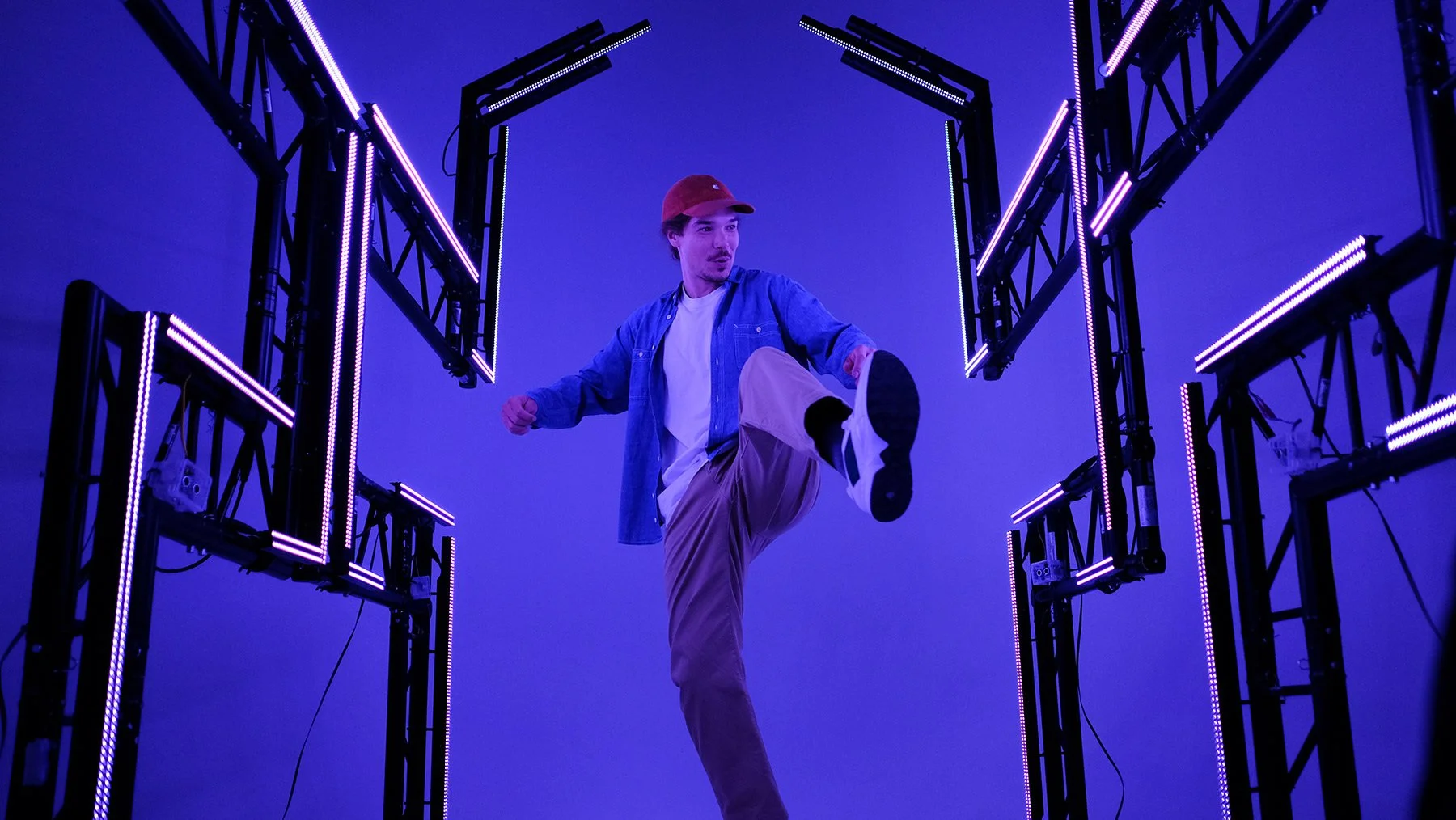
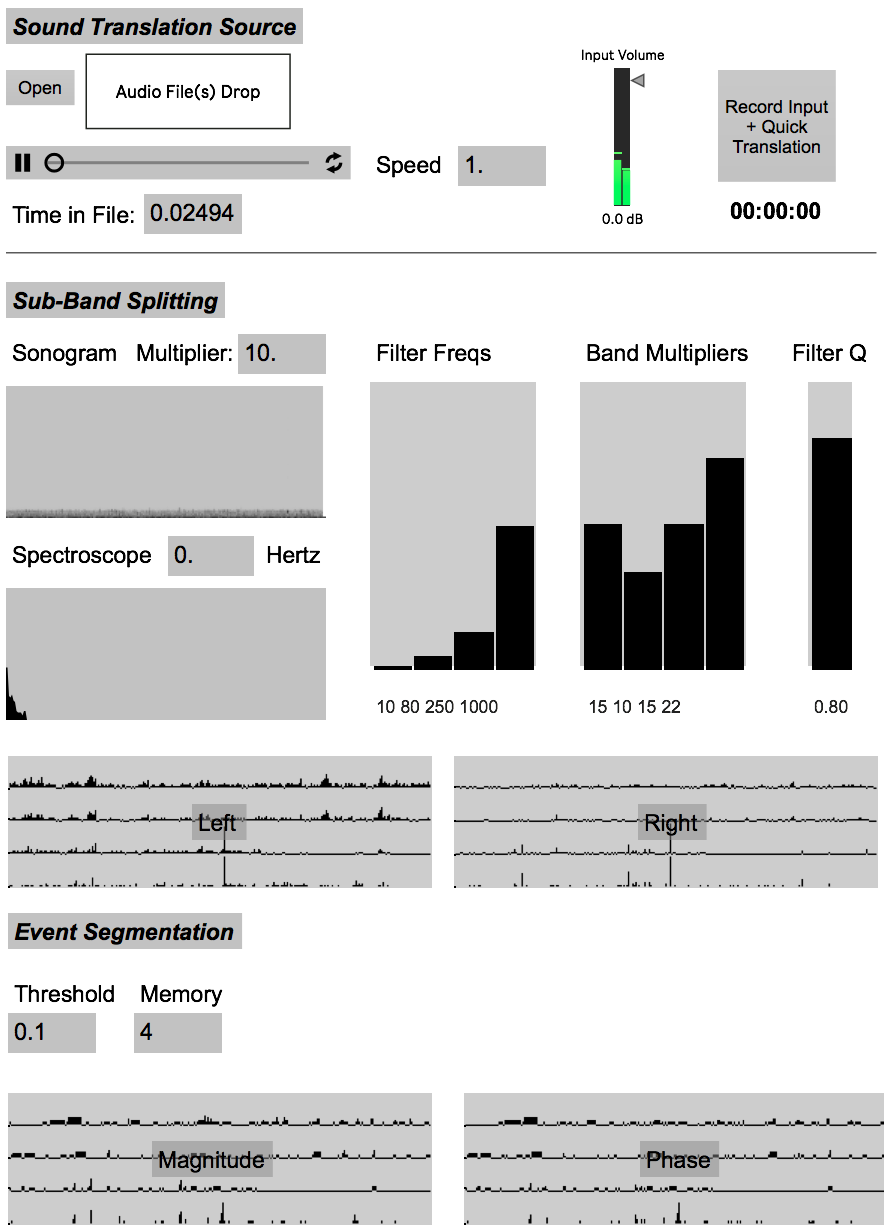
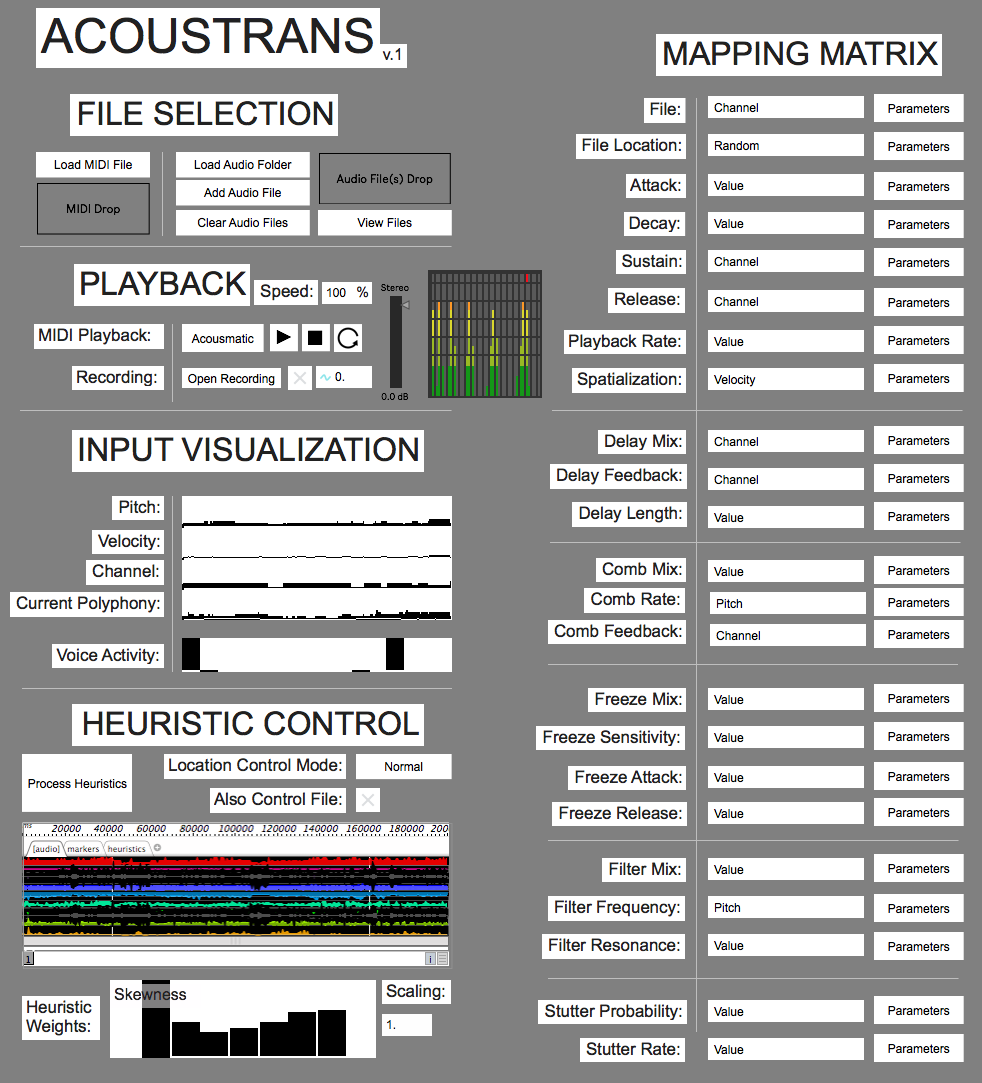
AcousTrans (Acousmatic Translator) allows a user to load in a source stereo audio file (field recording or other environmental recording) and a destination corpus of audio files and interactively map the events, gestures, and structure of the source onto the destination. What results is a stereo or multi-channel audio file with gestural, rhythmic, and/or structural similarities to the source file, but with entirely different timbral characteristics: those of the destination corpus.
After a processes of filtering and segmentation, the acoustic features embedded in each source event may be used to select a similar sound within a user-selected destination corpus via concatenative sound synthesis. Using a k-nearest neighbors search algorithm on a k-dimensional tree constructed from the acoustic features of segments of each audio file in the audio file corpus, the subvector of acoustic features for a source event is mapped to the most similar sound within the destination corpus. You can also customize the weighting of the features, which can be useful to “tune” the system depending on the particular source and destination sounds (for example, de-emphasizing fundamental frequency estimation if only using sounds with no clear pitch center)